Context
-
The Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO) this month granted market authorisation for NexCAR19, India’s first indigenously-developed CAR-T cell therapy, to ImmunoACT, a company incubated by IIT Bombay.
-
This paves the way for the commercial launch of this therapy in India, where it is expected to be available to cancer patients at a tenth of the cost abroad.
-
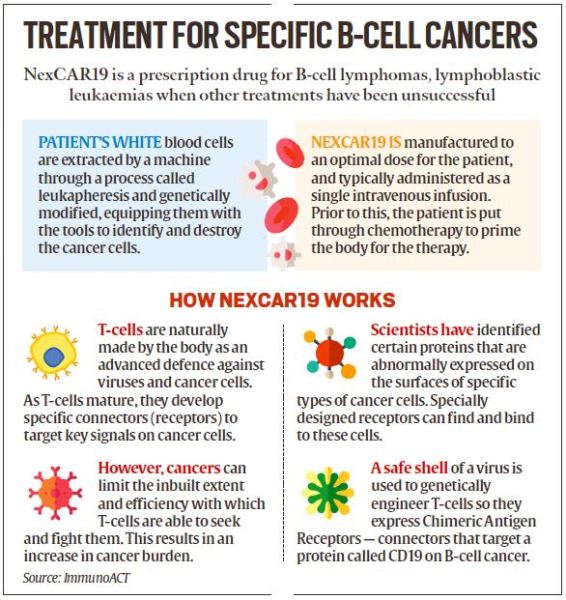
What is CAR-T cell therapy, and how do CAR-T cells find and destroy cancer cells?
- CAR-T is a revolutionary therapy that modifies immune cells, specifically T-cells, by turning them into potent cancer fighters known as CAR-T cells.
NexCAR19 India’s first CAR-T cell therapy - T-cells are special cells (white blood cells that find and fight illness and infection) whose primary function is cytotoxic, meaning it can kill other cells.
- In CAR-T therapy, we genetically modify them into cancer-fighting cells.
- These supercharged cells are then put back into the body, and they go after cancer cells — especially in blood cancers like leukaemia and lymphomas.
How effective and different is this from other cancer treatments like, say, chemotherapy?
- While chemotherapy and immunotherapy may add a few months or years to a cancer patient’s life, cell-and-gene therapy is designed to cure and provide lifelong benefit.
- It makes treatment easier with a one-time therapy [unlike several sessions of chemotherapy] that can be truly transformative [for a patient].
- It’s a lifeline for non-responsive cancer patients.
Is NexCAR19 a type of CAR-T therapy?
- NexCar19 is a type of CAR-T and gene therapy developed indigenously in India by ImmunoACT, which is a company incubated at IIT Bombay.
- Our therapy is designed to target cancer cells that carry the CD19 protein.
- This protein acts like a flag on cancer cells, which allows CAR-T cells to recognise and attach themselves to the cancer cells and start the process of elimination.
- Even some developed nations don’t have their own CAR-T therapies; they import them from the United States or Europe.
- India is now one of the first developing countries to have its indigenous CAR-T and gene therapy platform.
Who can get the NexCAR19 therapy?
- The therapy is for people with B-cell lymphomas who didn’t respond to standard treatments like chemotherapy, leading to relapse or recurrence of the cancer.
- The patient’s journey starts with a doctor’s prescription at the clinic, followed by donation of blood by the patient at a transfusion centre.
- The blood goes to the lab, where the T-cells are genetically modified.
- In a week to 10 days, these cells return to the clinic for patient reinfusion.
- Essentially, patients only need to give a blood sample at their clinic, and come back in 7-10 days for reinfusion.
- Recovery typically occurs within two weeks after one cycle of the treatment. In our data, approximately 70% of patients respond to the treatment, with variations between leukaemia and lymphoma cases.
- About 50% of these responsive patients achieve a complete response.
B-cell leukaemia is most common among children. Are they eligible for the therapy too?
- The paediatric trial phase is currently underway at the Tata Memorial Hospital, in collaboration with IIT-Bombay.
- Although the therapy for children will not be any different, for now, ImmunoACT has received CDSCO approval for use in patients aged 15 years and older.
Is India’s indigenous CAR-T cell therapy any more or less effective than CAR-T cell therapies abroad?
- Laboratory and animal studies have shown a unique quality of this product.
- Specifically, it leads to significantly lower drug-related toxicities.
- It causes minimal damage to neurons and the central nervous system, a condition known as neurotoxicity.
- Neurotoxicity can sometimes occur when CAR-T cells recognise the CD19 protein and enter the brain, potentially leading to life-threatening situations.
- The therapy also results in minimal Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS), which is characterised by inflammation and hyperinflammation in the body due to the death of a significant number of tumour cells, as CAR-T cells are designed to target and eliminate cancer cells.
- You can think of this like how the body responds to a virus such as SARS-CoV-2, where the immune response triggers an influx of certain proteins called cytokines, causing a lot of inflammation.
Will the treatment be covered by insurance?
- When a therapy is approved by regulatory agencies like CDSCO or DCGI, it typically should be covered by national insurance schemes and private insurance companies.
- However, since this is an expensive treatment, the extent of coverage and accessibility to insurance may vary.
Source: IE
Visit Abhiyan PEDIA (One of the Most Followed / Recommended) for UPSC Revisions: Click Here
IAS Abhiyan is now on Telegram: Click on the Below link to Join our Channels to stay Updated
IAS Abhiyan Official: Click Here to Join
For UPSC Mains Value Edition (Facts, Quotes, Best Practices, Case Studies): Click Here to Join